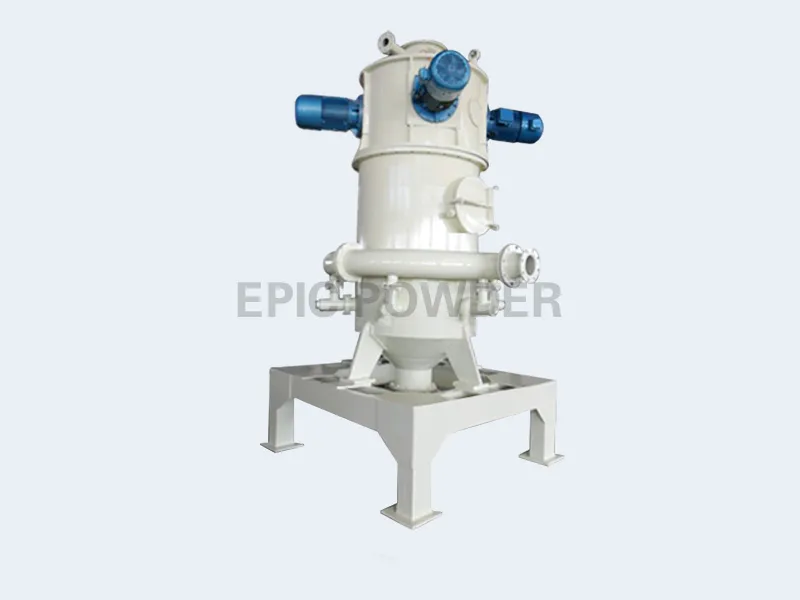
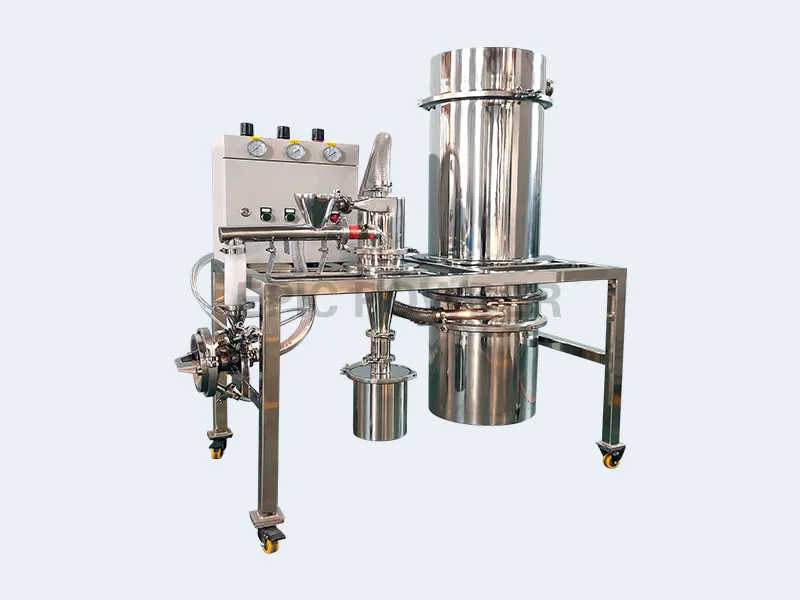
Air jet mills are used in many industries for particle size reduction. They are especially common in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. These mills use high-velocity air jets to micronize materials. They produce a fine powder with a narrow particle size distribution. Air jet mills have many advantages. But, they generate heat during operation. That is a major challenge. Excessive heat can harm the quality of the processed materials. It can also wear out equipment and raise energy use. So, it is crucial to prevent heat during processing. This optimizes performance and ensures product integrity.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
What is an Air Jet Mill?
An air jet mill is a type of milling equipment. It uses high-speed jets of compressed air to accelerate and reduce the size of particles. The principle is simple. Introduce raw materials into a milling chamber. There, intense airflow will subject them to it. Particle collisions and impacts with the chamber walls cause fragmentation and size reduction.
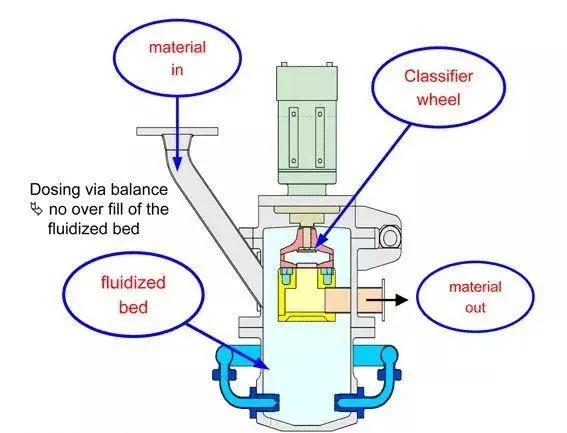
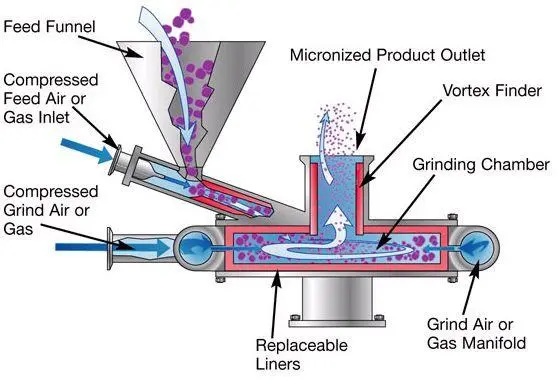
Key Components of an Air Jet Mill
- Milling Chamber: The central area where the milling action takes place.
- Air Nozzles: Designed to create high-velocity air jets that propel particles.
- Classifying Wheel: Separates fine particles from coarser ones based on size.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: Allow raw materials in and finished products out.
- Air Compressor: An air jet mill’s air compressor provides compressed air. It is needed to grind and separate materials.
Applications of Air Jet Mills
Applications of Air Jet Mills
Air jet mills are used in many applications. They can produce fine powders without adding moisture or contaminants. Key applications include:
Pharmaceuticals: For producing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with precise particle sizes.
Food Processing: Milling spices, herbs, and other foods. It must preserve their flavor and nutrients.
Chemical Manufacturing: For producing fine chemicals and pigments used in coatings and plastics.
Air jet mills are vital in making medicines, foods, and chemicals. They must control temperatures precisely to ensure product quality and safety.
Heat Generation in Air Jet Milling
Sources of Heat
Heat generation during air jet milling primarily arises from several factors:
- Friction: Collisions between particles and the chamber walls generate heat.
- Impact Forces: High-velocity air jets release kinetic energy as heat when particles collide at high speeds.
- Energy Consumption: Compressing air and maintaining airflow generates heat.
Effects of Excessive Heat
Excessive heat during processing can lead to several detrimental effects:
- Material Degradation: Sensitive materials may degrade from heat. This affects their chemical properties and efficacy.
- Product Quality Issues: High temperatures can change particles, harming quality.
- Equipment Wear: High temperatures can speed up wear on the air jet mill’s parts. This will raise maintenance costs.
Strategies to Prevent Heat Generation
To manage heat in air jet milling, implement various strategies:
Cooling Techniques
Air Jet Cooling
Using extra air jets for cooling can help remove heat from processing. This method directs cool air into the milling chamber or around critical parts.
Implementation: Install nozzles to blow cool air into the milling chamber.
Benefits: This strategy lowers temperatures. It does so without adding moisture or contaminants to the processed material.
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling systems can be added to air jet mills. They will improve temperature control.
Overview: Circulating coolant around critical components absorbs excess heat generated during operation.
Advantages: Liquid cooling systems manage heat better than air cooling. They have higher thermal conductivity.
Environmental Control
Ambient Temperature Regulation
A controlled ambient temperature in the workspace is key for thermal management.
- HVAC Systems: Installing HVAC systems helps regulate the milling area’s temperature.
- Impact on Performance: A cooler environment reduces thermal stress on machines and materials.
Ventilation Solutions
Proper ventilation is crucial for dissipating heat generated during milling operations.
- Design Considerations: Position fans or vents to ensure good airflow around the machines.
- Benefits: Better ventilation lowers temperatures and boosts comfort in long machining jobs.
Monitoring Systems
Temperature Sensors and Feedback Mechanisms
Implementing real-time monitoring systems allows operators to track temperatures dynamically throughout processing.
- Types of Sensors: Use thermocouples or infrared sensors at key points in the milling system. They will provide accurate temperature readings.
- Feedback Loops: Use feedback systems that adjust operations based on temperature data. For example, reduce feed rates if temperatures exceed a threshold.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Pharmaceutical Industry Example
In a pharmaceutical plant, operators faced heat issues with an air jet mill used for API production. It was degrading the product. They used liquid cooling and lower feed rates to reduce temperature fluctuations. Product quality improved. This led to higher yields and less waste.
Food Processing Example
A spice grinding company adopted new cooling methods. They used phase change materials in their air jet mill design. This approach let them keep consistent temperatures during processing. It preserved the flavor. They reported better product quality and customer satisfaction. Their spices had improved flavor profiles.
Conclusion
Managing heat in air jet mills is vital. It ensures efficient processing and high product quality. Manufacturers can optimize their air jet milling processes. They should understand heat sources and use effective strategies. These include cooling, material selection, and operational adjustments.
Advanced monitoring systems improve temperature control. They let operators make real-time adjustments to reduce overheating risks. With efficient manufacturing on the rise, air jet milling’s thermal management will be key. It is key to optimal performance and product quality.